Present Perfect Tense in English Grammar:
Present Perfect Tense is used to express an action just completed (presently completed, not very past) Past time adverbials are not used with The Present Perfect Tense.
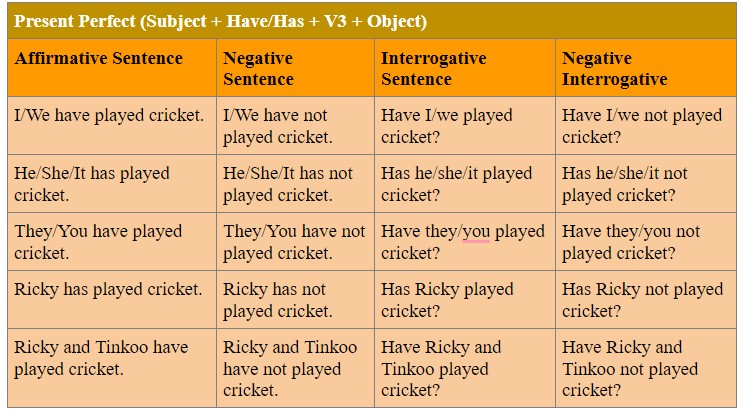
The Present Perfect Structure and Formula: (Rules)
Signal Words:
It is essential to focus on signal words because they help us identify the correct tense in a sentence. The signal words for the Present Perfect Tense are:
just, recently, lately, often, so far, never, ever, till now, up to now, yet, not yet, already, for, since, today, this week/month/year….,
Usage of the Present Perfect Tense:
It is used:
To express an action just completed (presently completed, not very past).
Examples:
- I have just written a letter.
- My friend has recently gone to the US.
- I have not yet completed my graduation.
- She has already sent me books.
To express an action that began in the past and is going on (incomplete) at present.
Examples:
- Smitha has worked in this college for five years. (Still working in the same college)
- We have lived in Warangal for thirty years. (Still living in Warangal)
- She has been in London for two weeks. (Still there in London)
More Examples: (Observe the signal words)
- Sheela has just come from the office.
- He has often told him not to do that.
- Have you ever seen Sheela?
- He has never seen such wonderful things.
- Has Snehit come yet?
- He has not come until now.
- His brother has already come.
- Anuradha has been ill since last week.
- He has not met his friend for two months.
- My friend has met me this week.
- The P.M. has visited Hyderabad this month.
The Present Perfect Vs. The Past Simple
The students of ESL often get confused with the Past Simple and Present Perfect Tense. But they are no so difficult as we are afraid of. Observe the few points mentioned below and find out the differences.
Note: 1
Present Perfect Tense is related to the present time.
Past Simple is Tense related to past time.
Examples:
- He has gone to Market (means not yet returned)
- He went to Market (means went to the market and came back)
- The door has opened (still it is open)
- The door opened (not kept open now)
- I have seen the film ‘Bahubali’ (still it is shown in a theatre)
- I saw the film ‘The Fifth Element’ (it is not shown in a theatre now)
Note: 2
Past time adverbials are not used with The Present Perfect Tense.
But these adverbials like yesterday, last week/month/year, in 2019 etc., are used with the Past Simple Tense.
Examples:
- I have received a letter yesterday (wrong) But
- I have received a letter. (right)
- I received a letter yesterday. (right)
- Usha has gone to Tiruvuru last week. (wrong) But
- Usha has gone to Tiruvuru (right)
- Usha went to Tiruvur last week(right)
- Shakespeare has written 37 dramas in the 16th century. (wrong) But
- Shakespeare has written 37 dramas. (right)
- Shakespeare wrote 37 dramas in the 16th century. (right)
Past actions can also be expressed in Present Perfect but we should not mention time.
Note: 3
The interrogative word When is used with Past Simple but not with Present Perfect in questions.
Examples:
- When have you informed me? (wrong)
- When did you inform me? (right)


Comments are closed.