English Phonetic Alphabet
Here in this article, you find the basic knowledge of 26 letters of the English alphabet of four types and 44 different phonic sounds or phonetic alphabet developed by the International Phonetic Alphabet.
The English word “alphabet” has been formed from the Latin word “alphabetum” which in turn originated from the first two letters of the Greek alphabet, “alpha” and “beta”. The English alphabet consists of 26 letters and 44 different sounds.
Generally, we find four types of the alphabet used in the English Language.
They are:

These letters of the alphabet in English are divided into
Vowels: (5 letters)
A E I O U
Consonants: (19 letters)
B C D F G H J K L M N P Q R S T V X Z
Semi-vowels: (2 letters)
W Y (These two letters can be used as vowels and consonants)
W is used as a vowel in the words like – saw, raw, row, crow etc.,
W is used as a consonant in the words like – was, who, when, what, whether etc.,
Y is used as a vowel in the words like – sky, why, fly, my cry etc.,
Y is used as a consonant in the words like – yarn, yearning, yoke, you etc.,
A more detailed chart is provided below wherein you find capital letters, small letters with their phonetic symbols, and how to pronounce them.

The English alphabet contains 26 letters which individually and in combination represent 44 different phonic sounds.
These 44 phonetic sounds in English which are also called phonemes or phonetic symbols mentioned here are in line with the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA).
Since English is not a phonetic language, these IPA symbols are really helpful for the learners of the language.
The English language seems to be very complicated because of its spelling rules and silent letters. So, the IPA helps to learn the correct sounds, word stress and pronunciation.
These 44 phonetic symbols can be divided into two major categories – they are
Vowel sounds and Consonant sounds
Vowel Sounds:
There are five letters of vowels used to make 20 different phonemes or phonetic symbols in the English language.
And these vowel sounds have been divided into three categories for the sake of easy understanding.
They are:
7 short vowels:
Short vowel symbols in the IPA are /ɪ/-pit, /e/-pet, /æ/-pat, /ʌ/-cut, /ʊ/-put, /ɒ/-dog, /ə/-about.
5 long vowels:
Long vowel symbols in the IPA are /i:/-week, /ɑ:/-hard,/ɔ:/-fork,/ɜ:/-heard, /u:/-boot.
and 8 Diphthongs (two short vowels joined together):
Diphthong vowel symbols in the IPA are /eɪ/-place, /oʊ/-home, /aʊ/-mouse, /ɪə/-clear, /eə/-care, /ɔɪ/-boy, /aɪ/-find, /ʊə/-tour.
Short Vowels
| (IPA Symbol) | Common spelling | Word examples |
| /æ/ | a – cat | Cat, hand, nap, flat, have |
| /ə/ | a – again | Alive, mother, attack, maker, doctor |
| /e/ | e – egg | Went, intend, send, letter, head, get, said |
| /i/ | i – igloo | sit, him, film, women, busy, build, hymn, |
| /ɒ/ | o – orange | Rob, top, watch, squat, sausage, not, jog, hop |
| /ʌ/ | u – mug | Fun, love, money, one, London, come. cup, double, monk |
| /u/ | oo – book | Put, look, should, cook, book, look, good, should, wood |
Long Vowels
| IPA Symbol | Common spelling | Word examples |
| /ɑ:/ | ɑɑ – car | Fast, hard, bath, car, art, hard |
| /i:/ | ee – sheep | Need, beat, team, sea, me, free |
| /ɜ:/ | ii – bird | Nurse, heard, third, turn. |
| /ɔ:/ | oo – door | Talk, law, yawn, jaw, saw, score, four |
| /u:/ | uu – shoot | Few, boot, lose, gloomy, fruit, chew. |
Diphthong Vowels
| IPA Symbol | Word examples |
| /ɪə/ | Near, ear, clear, tear, beer, fear |
| /eə/ | Hair, there, care, stairs, pear |
| /eɪ/ | Face, space, rain, case, eight |
| /ɔɪ/ | Joy, employ, toy, coil, oyster |
| /aɪ/ | My, sight, pride, kind, flight |
| /əʊ/ | No, don’t, stones, alone, hole |
| /aʊ/ | Mouth, house, brown, cow, out |
| /ʊə/ | Tourist, tour, pure |
Consonant Sounds:
There are 21 consonants in English which represent 24 different consonant phonic sounds. Like vowels, the consonant sounds have also been divided into several categories like
Plosives,
Fricatives,
Affricates,
Nasals,
Approximants and
Lateral.
Plosives: These are consonant sounds that are made by stopping air flowing out of the mouth, and then suddenly releasing it.
Voiced: /p/, /t/, /k/
Voiceless: /b/, /d/, /g/
| IPA Symbol | Common spelling | Word examples | Place of articulation |
| /p/ | p – pig |
Pin, cap, purpose, pause, pen, pencil | Bilabial |
| /b/ | b – ball | Bag, bubble, build, robe. | Bilabial |
| /t/ | t – tap | Time, train, tow, late. | Alveolar |
| /d/ | d – dog | Door, day, drive, down, feed. | Alveolar |
| /k/ | k – kite | Cash, quick, cricket, sock. | Velar |
| /g/ | g – grapes | Girl, green, grass, flag. | Velar |
Fricatives: These are consonants produced when air passes through a narrow channel between two articulators.
Voiced: /v/,/ð//z/, /ʒ/, /h/
Voiceless: /f/, /θ//s/,/ʃ/
| IPA Symbol | Common spelling | Word examples | Place of articulation |
| /f/ | f – fan | Full, Friday, fish, knife. | Labiodental |
| /v/ | v – van | Vest, village, view, cave. | Labiodental |
| /θ/ | th – thin | Thought, think, bath. | Dental |
| /ð/ | th – then | There, those, brothers, others. | Dental |
| /s/ | s – sea | Seal, missing, face | Alveolar |
| /z/ | z – zebra | Zoo, crazy, lazy, zigzag, nose. | Alveolar |
| /ʃ/ | sh – shark | Shirt, rush, shop, cash. | Palatal |
| /ʒ/ | s – vision | Television, delusion, casual | Palato-alveolar |
| /h/ | h – hat | High, help, hello. | Glottal |
Affricates: These are also called semi plosives. These consonant sounds begin as a stop (sound with complete obstruction of the breath stream) and conclude with a fricative (sound with incomplete closure and a sound of friction).
Voiced: /dʒ/
Voiceless: /ʈʃ/
| IPA Symbol | Common spelling | Word examples | Place of articulation |
| /ʈʃ/ | ch – catch | Choose, cheese, church, watch. | Palatal |
| /dʒ/ | j – joke | Joy, juggle, juice, stage. | Palato-alveolar
|
Nasals: These are consonant sounds in which the escaping air passes through the nasal cavity.
Voiced: /m/, /n/, /ŋ
| IPA Symbol | Common spelling | Word examples | Place of articulation |
| /m/ | m – moon | Room, mother, mad, more. | Bilabial |
| /n/ | n – noon | Now, nobody, knew, turn. | Alveolar |
| /ŋ/ | ng – sing | King, thing, song, swimming. | Velar |
Approximants: These speech sounds are formed by the passage of air between two articulators (such as the lips or tongue) which are close but not touching.
Voiced: /r/, /j/,/w/,
| IPA Symbol | Common spelling | Word examples | Place of articulation |
| /r/ | r – real | Road, roses, river, ring, ride. | Alveolar-retroflex |
| /j/ | y – you | Yellow, usual, tune, yesterday, yard. | Palatal |
| /w/ | w -web | Wall, walk, wine, world. | Labial-velar |
Lateral: This consonant sound occurs when the tongue blocks the middle of your mouth so that air has to pass around the sides
Voiced: /l/
| IPA Symbol | Common spelling | Word examples | Place of articulation | |
| /l/ | l – love | Law, lots, leap, long, pill, cold, chill, melt | Alveolar-lateral |
Note:
The following 3 consonant letters have not been mentioned in the above list because they don’t have their own unique sound.
c borrows the sounds of /k/ and /s/
q is the combination of /kw/
x is the combination of /ks/ (box) or /gz/ (exist)
The names for the main places of articulation are shown in the diagram and the table below to understand the phonetic transcription in an easy manner.
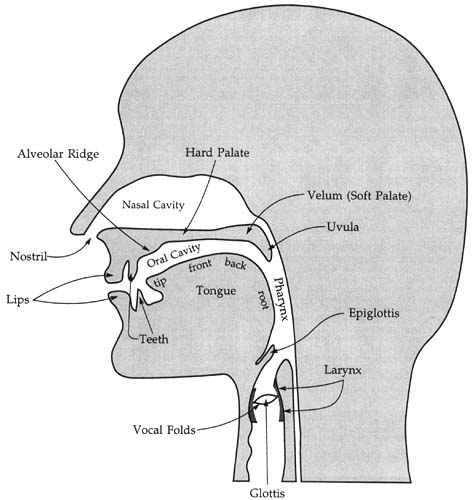
image source: internet
| Place | Description |
|---|---|
| Bilabial | both lips |
| Labiodental | lower lip against upper teeth |
| Dental | tongue tip against upper teeth |
| Alveolar | tongue tip against teeth ridge |
| Alveolar-lateral | tongue tip against teeth ridge but with sides lowered |
| Alveolar-retroflex | tongue tip curled back near teeth ridge |
| Palato-alveolar | tongue tip slightly retracted from teeth ridge |
| Palatal | tongue blade against the hard palate |
| Velar | back of the tongue against the soft palate |
| Glottal | vocal fold closure in the larynx |
Recommended readings:



Comments are closed.