Present Simple Tense in English Grammar:
The Present Simple is also called Present Indefinite or Simple Present Tense. It generally describes present routine events, facts, truths etc.,
Present Simple Tense Structure and Formula: (Rules)
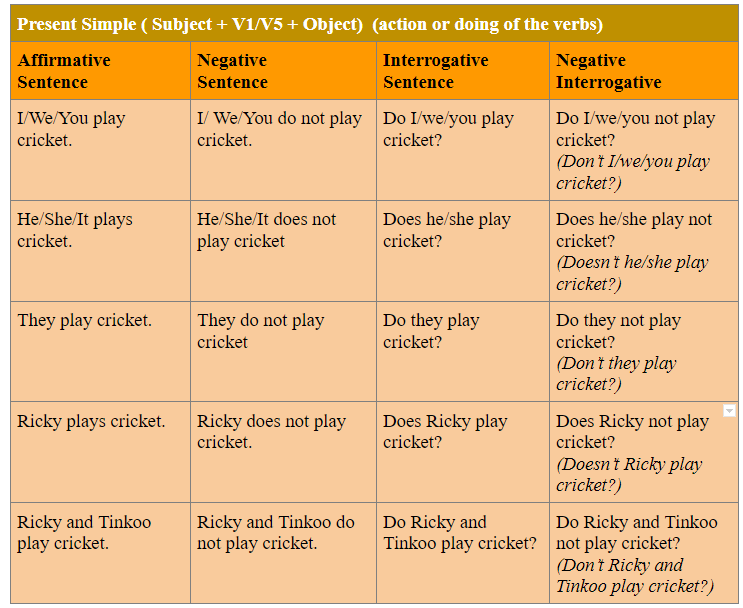
The following sentences are also considered Present Simple: (with the use of do, does, can, may, must, have to, has to)
Examples:
- They do Yoga.
- He does Karate.
- I can sing a song.
- He may not participate in the event.
- You must go there.
- He has to obey the orders.
- You have to attend class.
Signal Words:
It is essentialt to focus on signal words because they help us identify the correct tense in a sentence. The signal words for the Present Simple Tense are:
every morning/evening/day/week/month/year/summer/winter…,
in the mornings/ evenings/summer/winter….,
on Sundays/Mondays..,
every Sunday/Monday….,
once in a week/month/year……,
always, normally, frequently, regularly, irregularly, rarely, usually, occasionally, daily, seldom, never, often, sometimes…,
Usage of the Present Simple Tense:
It is used:
To express Habitual Actions/Routine Activities.
Examples:
- He usually goes to college by bus.
- He sometimes sits in the front row.
- Mary goes to church every Sunday.
- She always wears black sarees.
- The boys play in the evenings.
- My father reads two newspapers daily.
To express Universal Truths and Scientific facts.
Examples:
- The Sun rises in the East.
- The Earth moves around the sun.
- Stars shine brightly.
- Ice is cold.
- Water freezes at 0 degrees Centigrade.
To express Quotations and Proverbs.
Examples:
- Necessity is the mother of invention.
- All that glitters is not gold.
- Practice makes a man perfect.
- A friend in need is a friend indeed.
To express Future Events when they are scheduled (especially official programmes).
Examples:
- The Prime Minister visits Warangal next month.
- The train arrives in ten minutes.
- The school reopens on Monday.
- They leave for Madras next week.
To express Past Events in narration for vivid description.
Examples:
- Hamlet meets his father’s ghost and learns the truth about his uncle.
- They go to the station and buy the tickets.
- Sita asks her sons not to misunderstand Rama. She further says that time reveals everything.
To express Likes, Dislikes and Professional Activities.
Examples:
- I like to play chess.
- She doesn’t like playing games.
- He works in a bank.
In Sports Commentaries like cricket.
Examples:
- Dhoni jumps out and hits over the point for a huge six.
- Jadeja cuts the ball to the deep point fielder and takes a single.
- Dhoni plays the ball on the offside and takes a single.
In Newspaper Headlines.
Examples:
- The Prime Minister of India welcomes the US President.
- PM Modi launches Rs. 20,050 crore scheme for the fisheries sector.
In Imperative Sentences.
Examples:
- Close the window, please.
- Submit your photograph immediately.
- Improve your handwriting.
In Type – I Probable Conditional Clause.
Examples:
- If you play well you will win the match.
- If she asks me I can help her.
In Exclamatory Sentences beginning with there and here.
Examples:
- Here comes the bus!
- There he goes!
Also, learn the following related to Present Simple:
‘Be’ forms (am, is, are) can be used as main verbs as well as auxiliary verbs. In the Present Simple Tense, we use them as main verbs.
Examples:
- I am a teacher.
- She is not a doctor.
- Are we eligible?
- Aren’t they sportsmen?
Let’s see it in a more detailed manner.
| ‘Be’ forms: as main verbs in Present Simple Tense (Am, Is, Are) | ||||||
| Affirmative Sentence | Negative Sentence | Interrogative Sentence | Negative Interrogative | |||
| I am | I’m | I am not | Am I? | Am I not | Aren’t I?Ain’t I? | |
| We are | We’re | We are not | We aren’t | Are we? | Are we not? | Aren’t we? |
| You are | You’re | You are not | You aren’t | Are you? | Are you not? | Aren’t you? |
| He is | He’s | He is not | He isn’t | Is he? | Is he not? | Isn’t he? |
| She is | She’s | She is not | She isn’t | Is she? | Is she not? | Isn’t she? |
| It is | It’s | It is not | It isn’t | Is it? | Is it not? | Isn’t it? |
| They are | They’re | They are not | They aren’t | Are they? | Are they not? | Aren’t they? |
‘Have’ forms (have, has) can be used as main verbs as well as auxiliary verbs. In the Present Simple Tense, we use them as main verbs.
Examples:
- I have a car.
- She has no Scooty. (She hasn’t any bike)
- Have they proper uniforms? (Do they have proper uniforms?)
- Haven’t we a complete time-table? (Don’t we have a complete time-table?)
Let’s see it in a more detailed manner.
| ‘Have’ forms: as main verbs in Present Simple Tense. (Have, Has) | ||||||
| Affirmative Sentence | Negative Sentence | Interrogative Sentence | Negative Interrogative | |||
| I have | I’ve | I have no
I’ve no |
I haven’t any | Have I?
Do I have? |
Have I not | Haven’t I?
Don’t I have? |
| We have | We’ve | We have no We’ve no |
We haven’t any | Have we?
Do we have? |
Have we not | Haven’t we?
Don’t we have? |
| You have | You’ve | You have no
You’ve no |
You haven’t any | Have you?
Do you have? |
Have you not | Haven’t you?
Don’t you have? |
| He has | He’s | He has no
He’s no |
He hasn’t any | Has he?
Does he have? |
Has he not | Hasn’t he? Doesn’t he have? |
| She has | She’s | She has no
She’s no |
She hasn’t any | Has she?
Does she have? |
Has she not | Hasn’t she?
Doesn’t she have? |
| It has | It’s | It has no
It’s no |
It hasn’t any | Has it?
Does it have? |
Has it not | Hasn’t it?
Doesn’t it have? |
| They have | They’ve | They have no
They’ve no |
They haven’t any | Have they?
Do they have? |
Have they not | Haven’t they?
Don’t they have? |
Contractions:
Contractions that are generally used in the Present Simple Tense with the forms of be, have and do.
| Regular | Contraction |
| am + not | aren’t (not amn’t) |
| is + not | isn’t |
| are + not | aren’t |
| have + not | haven’t |
| has + not | hasn’t |
| do + not | don’t |
| does + not | doesn’t |
| I + am, I + have | I’m, I’ve |
| you + are, you + have | you’re, you’ve |
| we + are, we + have | we’re, we’ve |
| he + is, he + has | he’s |
| she + is, she + has | she’s |
| it + is, it + has | it’s |
| they + are, they + have | they’re, they’ve |
| can + not | can’t |
| may + not | mayn’t |
| must + not | mustn’t |
Spelling Rules:
We add –s or –es to the verb in third person singular number (or V5). -s is added in general, but -es is added in the following way.
We add –es to the verb that ends in ss,
Examples:
kiss – kisses, dress – dresses, miss – misses, bless – blesses, guess – guesses
cross – crosses, Possess – possesses etc.,
We add –es to the verb that ends in –sh
Examples:
slash – slashes, flash – flashes, clash – classes, vanish – vanishes, punish – punishes
polish – polish, flourish – flourishes, accomplish – accomplishes etc.,
We add –es to the verb that ends in – ch
Examples:
catch – catches, clinch – clinches, clutch – clutches, teach – teaches
watch – watches, match – matches etc.,
We add –es to the verb that ends in – x
Examples:
relax – relaxes, box – boxes, suffix – suffixes, prefix – prefixes, perplex – perplexes, mix – mixes, xerox – xeroxes etc.,
We add –es to the verb that ends in – o
Examples:
do – does, go – goes solo – soloes, echo – echoes, forego – foregoes, veto – vetoes etc.,
If the verb ends in a consonant and –y we change –y into -i and add –es:
Examples:
carry – carries, try – tries, certify – certifies, satisfy – satisfies, clarify – clarifies, classify – classifies etc.,
But if the verb ends in a vowel before -y only -s.
Examples:
play – plays, misplay – misplays, outplay – outplays, overlay – overlays, destroy – destroys, betray – betrays etc.,


Comments are closed.